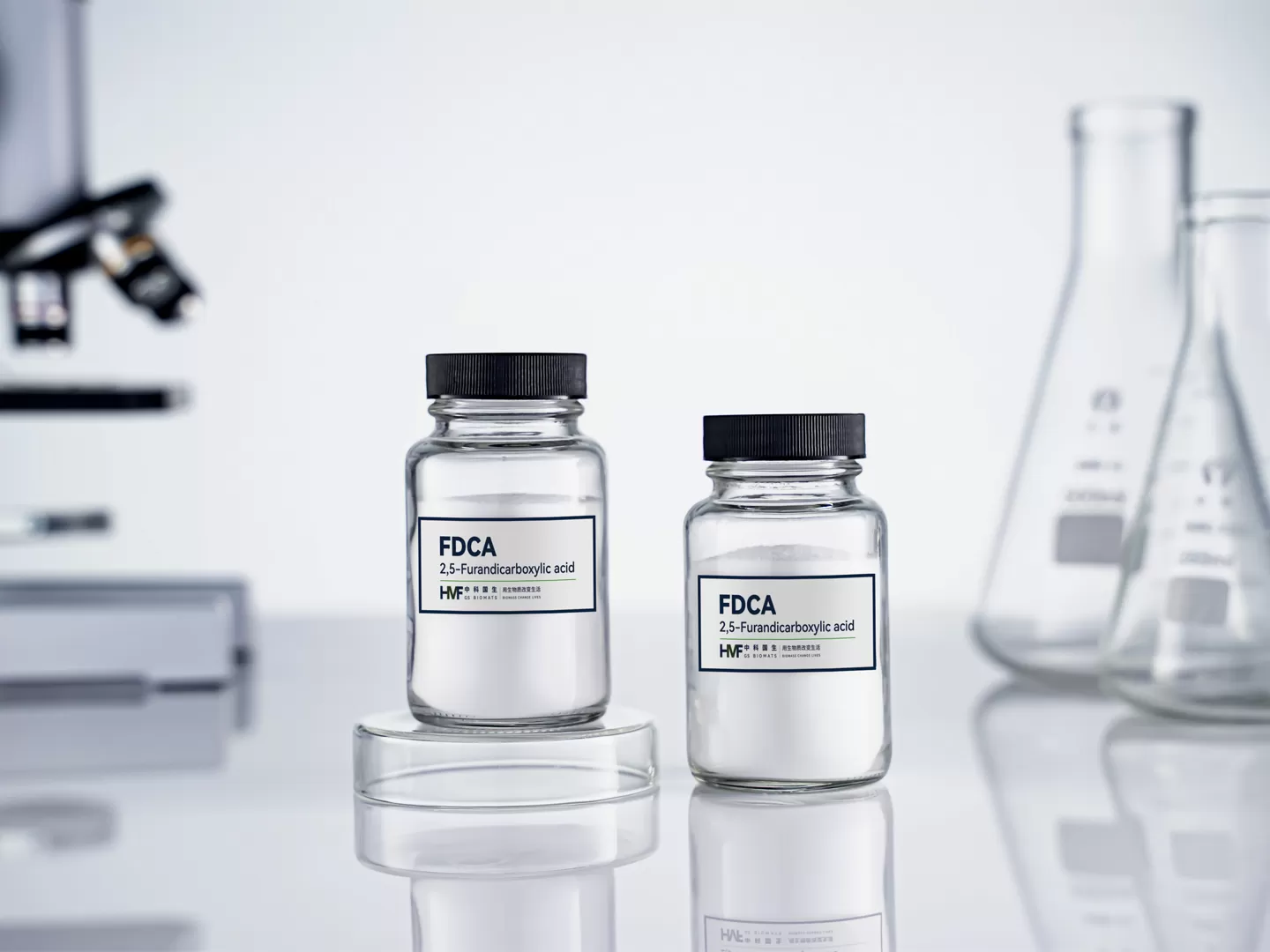
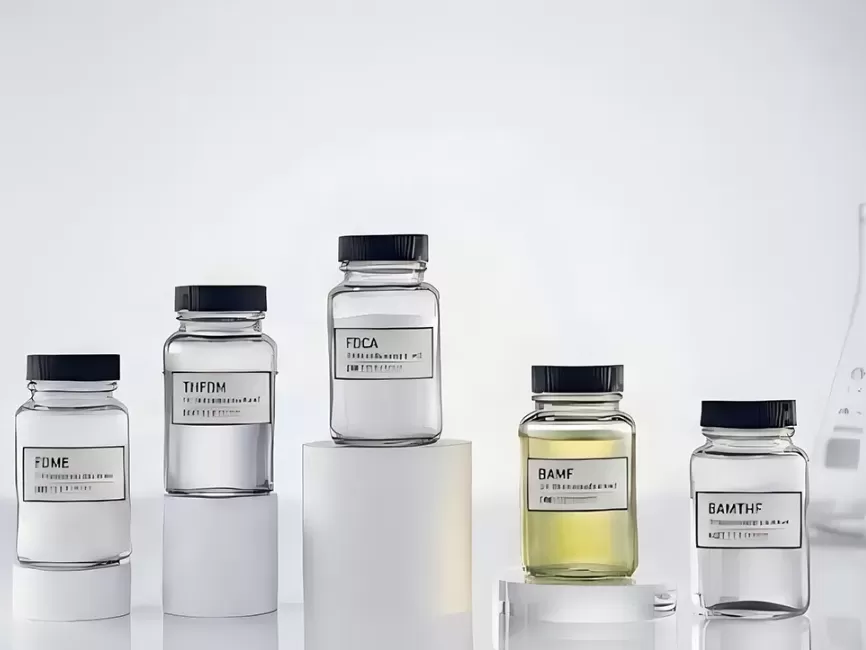
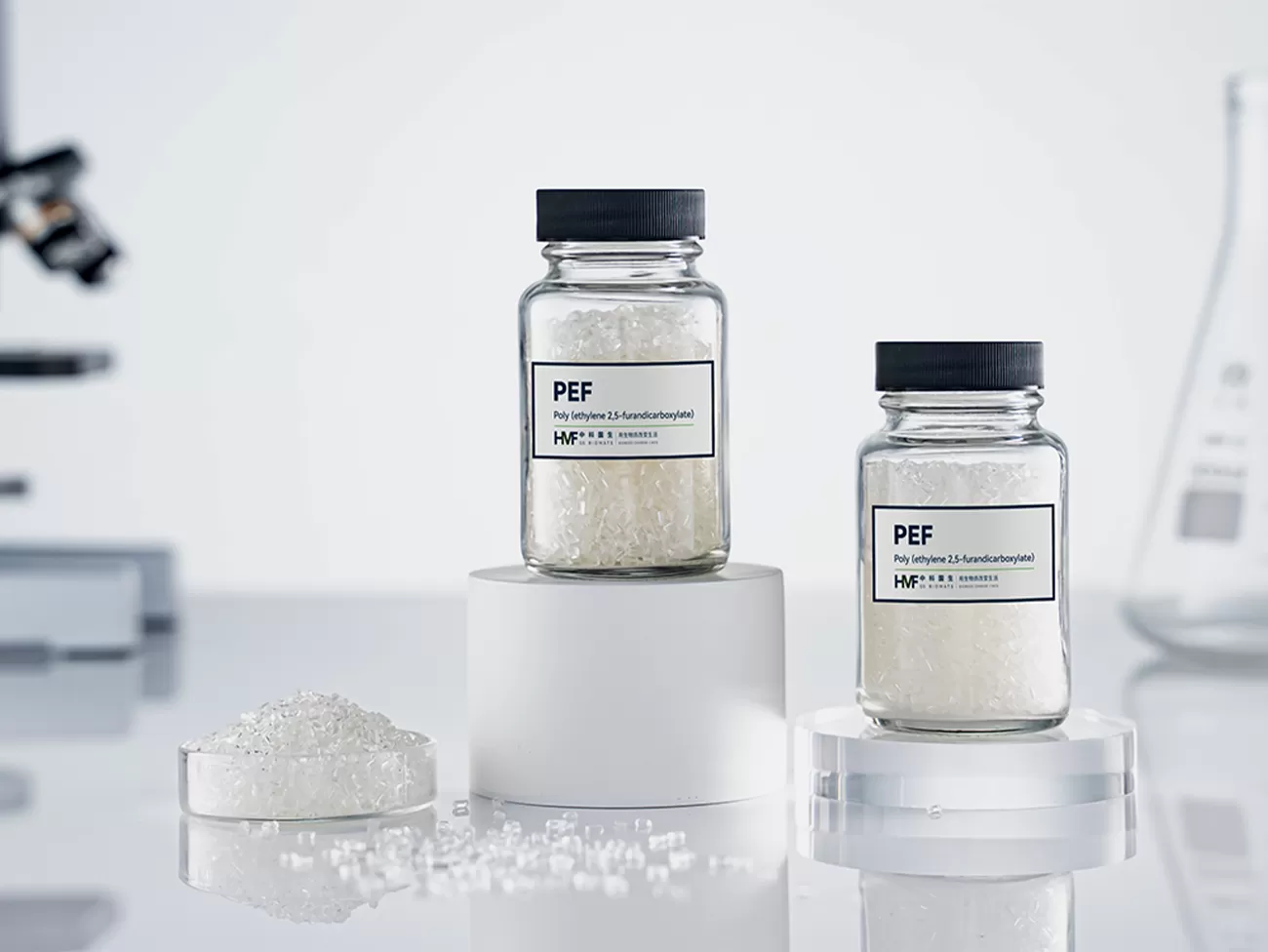
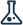FDCA (CAS 3238-40-2), recognized by the U.S. Department of Energy as one of the "Top 12 Building Block Chemicals for a Green Future," is a furandicarboxylic acid with a cyclic structure and reactivity comparable to terephthalic acid (PTA), serving as a key monomer for sustainable polymer applications.
As the most in-demand furan monomer, it provides a renewable alternative or complement to aromatic petrochemicals.
lts key polymer, poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate) (PEF), which is formed by polymerizing FDCA with ethylene glycol, delivers exceptional gas barrier properties for packaging, as well as antibacterial & mite-resistant, moisture-wicking, and UV-resistant features for fiber applications.
Beyond PEF, this renewable monomer also enables the development of bio-based nylons (PA), aramids (PPA), and elastomers, supporting a wide range of advanced polymer applications. Continuous improvements in FDCA production technology and cost efficiency are accelerating its global adoption as a sustainable and high-performance material.